
Relay Messaging: Best Deep Dive into Its Technology, Applications, and Impact 2024
Relay messaging in the age of digital communication, the ability to transmit information efficiently and reliably is essential. One critical communication technique that enables this is relay messaging. Relay messaging is a method of passing messages from one intermediary to another until the message reaches its final destination. This concept may seem straightforward, but the underlying technology and its applications span a wide array of industries, from telecommunications to the internet, logistics, and even space exploration.
What is Relay Messaging?
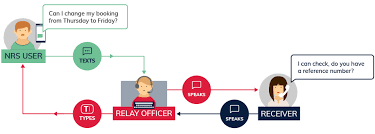
Relay messaging is the process by which messages or data are transmitted across multiple nodes, or relay points, before reaching their intended recipient. The nodes act as intermediaries, ensuring that the message can cover a wider distance, navigate through network restrictions, or maintain a high level of reliability and security. In its simplest form, relay messaging involves three core elements:
- The Sender: The entity that initiates the message.
- The Relay Node(s): The intermediary(s) that process and forward the message.
- The Receiver: The final destination where the message is delivered.
While the sender and receiver are often clear in most communication models, the relay nodes are where the magic happens. These intermediaries can be physical devices such as servers or software algorithms, depending on the type of network being used.
History of Relay Messaging
Relay messaging has roots in some of the earliest communication systems, such as semaphore lines, carrier pigeons, and even human couriers, where messengers would physically pass information from one person or location to another. However, with the invention of the telegraph in the 19th century, relay messaging entered the electronic era.
Samuel Morse’s telegraph system required repeaters to relay electrical signals across long distances. This was the precursor to modern relay systems, in which data is broken down into signals, transmitted across a network of nodes, and then reassembled at the destination. As communication technology advanced, relay systems became more sophisticated, leading to innovations in radio, satellite communications, and, eventually, the internet.
Types of Relay Messaging
Relay messaging today is used across different domains and can be categorized into several distinct types based on the technology and application:
- Telecommunications Relays: In telecommunications, relay stations are used to amplify or regenerate signals, enabling long-distance communication. Examples include radio and television broadcasts where relay towers ensure coverage over large geographical areas, and undersea cable repeaters that maintain signal integrity across oceans.
- Email Relays: Email servers frequently use relay messaging to transmit messages from one mail server to another. Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) relays are an example, where an email is forwarded through a series of servers before arriving at the recipient’s inbox. This system allows for efficient routing and error-checking, ensuring the message reaches its intended destination.
- Network Relays: In computer networking, relay messaging often involves routers and switches that direct data packets from one network to another. The Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) suite, which forms the backbone of the internet, uses relay-based routing to ensure that data packets navigate through complex global networks, reaching the correct device.
- Blockchain and Distributed Systems: In decentralized systems like blockchain networks, relay nodes play a crucial role in relaying transactions and blocks between different parts of the network. This ensures the integrity and consistency of data across distributed ledger systems, where trust and security are paramount.
- Space Relay Systems: Relay messaging is fundamental to space communication, where direct communication between distant spacecraft and Earth may not be possible. For instance, NASA’s Deep Space Network uses relay satellites to maintain communication with spacecraft like the Mars rovers. This method allows data to be transmitted across millions of miles in space, often using relay nodes on other planets or satellites.
How Relay Messaging Works
The exact process of relay messaging depends on the technology and application, but the general principles remain the same:
- Message Creation: The sender generates the message and encapsulates it in a format that can be transmitted. In digital systems, this often involves encoding the message into packets of data.
- Transmission to the First Relay: The message is sent to the first relay point, which could be a server, satellite, or network node. This transmission could be wired or wireless, depending on the communication medium.
- Processing at the Relay: The relay node processes the message, which may involve tasks like error checking, signal amplification, or encryption. In some systems, the relay node might also modify the message format to ensure compatibility with the next leg of the journey.
- Forwarding to the Next Node: Once processed, the relay forwards the message to the next node in the chain. This step is repeated until the message reaches its final destination.
- Message Reception and Acknowledgment: The message is finally delivered to the receiver. In many relay systems, an acknowledgment is sent back to the sender to confirm that the message was received successfully.

The Role of Security in Relay Messaging
Security is a critical concern in relay messaging, particularly in the digital age. As messages pass through multiple intermediaries, they can be vulnerable to interception, tampering, or delays. Several techniques are employed to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of messages in a relay system:
- Encryption: Messages can be encrypted at the source so that even if they are intercepted during transmission, they cannot be read or altered without the decryption key.
- Authentication: Both the sender and receiver may authenticate themselves to ensure that they are communicating with the intended party. This is common in email relays, where servers use domain-based authentication mechanisms like SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) to prevent spoofing.
- Error Correction and Integrity Checks: To prevent message corruption, relay systems often use checksums or hash functions to verify the integrity of the message at each stage of the transmission process.
- Redundancy: In systems where reliability is paramount, messages can be sent through multiple relay paths to ensure that if one path fails, the message can still reach its destination via an alternative route.
Applications of Relay Messaging
Relay messaging is a versatile technology with applications across many industries:
- Telecommunications: Relay stations, whether for radio, television, or cell networks, extend the reach of signals to rural and remote areas, ensuring widespread coverage.
- Email and Internet: Email relays are used by organizations and service providers to deliver messages efficiently. Meanwhile, internet data routing relies on relay principles to direct traffic through global networks.
- Military and Defense: Secure relay communication is essential for military operations, allowing for encrypted messages to be sent across distances without risking interception.
- Space Exploration: Space relay systems enable continuous communication with spacecraft on interplanetary missions, ensuring data and telemetry can be transmitted back to Earth for analysis.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: In logistics, relay messaging can be used to coordinate shipments, ensuring that real-time data about the movement of goods is communicated across the entire supply chain.
Future of Relay Messaging
As communication networks become more complex and global, the need for efficient and secure relay messaging will only increase. The proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT), where billions of devices need to communicate with each other, will require advanced relay systems to manage data traffic.
Similarly, as humanity ventures deeper into space, relay messaging will be crucial for maintaining communication with distant spacecraft and colonies. New innovations like quantum relays, which leverage quantum entanglement to transmit information instantaneously, could revolutionize this field in the coming decades.
In conclusion, relay messaging is an essential aspect of modern communication, serving as the backbone of many technologies we use today. From ensuring that emails arrive in our inbox to facilitating interstellar communication, the principles of relay messaging will continue to drive innovation and connectivity in the future.


